Cardiac Electrophysiology (EPS)
What is Cardiac Electrophysiology (EPS)?
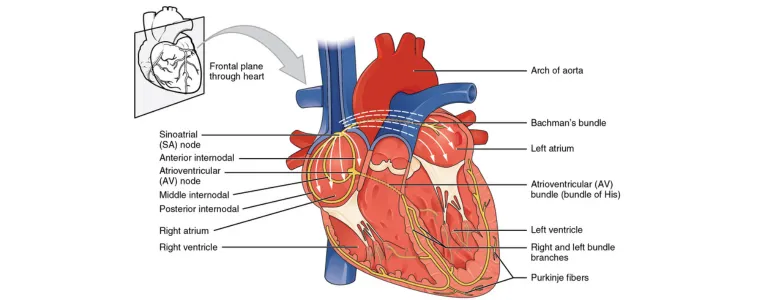
Cardiac Electrophysiology (EPS) is a specialized area of cardiology that focuses on diagnosing and treating abnormal heart rhythms, also known as arrhythmias. The heart’s electrical system controls the heartbeat, and any irregularities in this system can cause the heart to beat too quickly, too slowly, or erratically.
An Electrophysiology Study (EPS) is a minimally invasive test used to evaluate the electrical activity of the heart. During the procedure, thin, flexible wires called catheters are inserted into a vein (usually in the groin) and guided to the heart. These catheters record the electrical signals from the heart, allowing the electrophysiologist to identify the source of abnormal rhythms. EPS is a critical tool for diagnosing conditions like atrial fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia, and other arrhythmias, and it often guides treatment decisions such as ablation or device implantation.
Who Needs an Electrophysiology Study (EPS)?
An Electrophysiology Study (EPS) is recommended for individuals who experience symptoms of abnormal heart rhythms or have been diagnosed with arrhythmias that require further investigation. Some common reasons for undergoing an EPS include:
- Unexplained Fainting (Syncope): If a patient has episodes of fainting that may be related to a heart rhythm issue, an EPS can help determine if an abnormal rhythm is the cause.
- Tachycardia (Fast Heart Rate): For patients experiencing rapid heart rates, such as supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) or ventricular tachycardia (VT), an EPS can help identify the specific arrhythmia and its origin.
- Bradycardia (Slow Heart Rate): If the heart is beating too slowly, an EPS can help pinpoint the cause and guide the need for a pacemaker.
- Atrial Fibrillation (AFib): EPS is often used to map the electrical activity of the heart in patients with AFib, helping to determine the most effective treatment.
- Evaluation of Treatment Options: For patients with arrhythmias that are difficult to manage with medication, an EPS can help guide treatment decisions such as catheter ablation or the placement of a pacemaker or implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD).
- Risk Assessment: For patients at risk of sudden cardiac arrest due to life-threatening arrhythmias, an EPS can help assess the risk and determine the need for preventative treatments.
What is Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA)?
Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA) is a highly effective treatment for certain types of arrhythmias. It is a minimally invasive procedure that uses heat energy to destroy small areas of heart tissue responsible for abnormal electrical signals. By targeting the source of the arrhythmia, RFA can correct the heart’s rhythm and prevent the recurrence of irregular heartbeats.
How is RFA Performed?
- During the procedure, catheters are inserted into the veins and guided to the heart, similar to an EPS. The electrophysiologist then uses radiofrequency energy to create small, controlled burns in the heart tissue that is causing the arrhythmia. This disrupts the abnormal electrical pathway, allowing the heart to maintain a normal rhythm.
- RFA is typically used to treat arrhythmias such as atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, ventricular tachycardia, and supraventricular tachycardia (SVT).
- The procedure is minimally invasive, and most patients can return home the same day or within 24 hours. Recovery is usually quick, with many patients resuming normal activities within a few days.
Benefits of Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA)
- High Success Rate: RFA is highly effective, with many patients experiencing long-term relief from arrhythmias.
- Minimally Invasive: The procedure requires only small punctures for the catheters, making recovery time faster and reducing the risk of complications.
- Reduced Need for Medications: After successful ablation, many patients can reduce or eliminate the need for anti-arrhythmic medications.
Who is a Candidate for RFA?
Patients with recurrent or persistent arrhythmias that have not responded well to medications are ideal candidates for RFA. It is also recommended for those who prefer a more permanent solution to arrhythmias, as the procedure can eliminate or significantly reduce the occurrence of abnormal heart rhythms.
At Dr. Javed’s Heart Rhythm Clinic, we use state-of-the-art technology to perform Electrophysiology Studies and Radiofrequency Ablation, offering a comprehensive approach to diagnosing and treating arrhythmias. Our goal is to provide patients with the best possible care and improve their quality of life by restoring a normal heart rhythm.
